EOS Whitepaper
Abstract
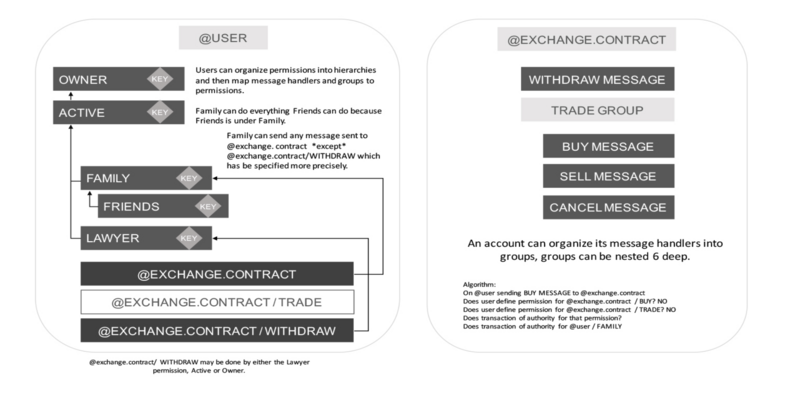
The EOS.IO software introduces a new blockchain architecture designed to enable vertical and horizontal scaling of decentralized applications. This is achieved by creating an operating system-like construct upon which applications can be built. The software provides accounts, authentication, databases, asynchronous communication, and the scheduling of applications across many of CPU cores or clusters. The resulting technology is a blockchain architecture that may ultimately scale to millions of transactions per second, eliminates user fees, and allows for quick and easy deployment and maintenance of decentralized applications, in the context of a governed blockchain.
Introduction
The notions of digital cash and smart contracting have been known for a long time, yet only in recent times have strides been taken with respect to implementation.
This paper introduces the EOS.IO software underlying EOS as a new platform for general value and contracting.
EOS is presented against a backdrop of three existing champions because (a) they represent a broad range of opinions as to the Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) space, (b) are large enough to matter, and (c) are familiar to the author.
Bitcoin (Nakamoto 2008) seemed to be the word on a blockchain that promised the inspirations of both digital cash and smart contracts. Although it captured the attention of the cypherpunks, media and hodlers, it failed to make a mark on business.
Ethereum (Woods 2014) attempted to fulfill the smart contract promise with an “unstoppable world computer” while Bitshares (Larimer et al 2014) strove to open up the market for tradeable assets. Hundreds of alternative Bitcoin blockchains or altcoins strove to make a small difference seem louder.
Corda (Brown et al 2016) backed away from blockchain entirely and explored party to party workflow solutions.
We are tantalisingly close but no prize has yet been awarded - by the end-users. It is timely to then take a fresh look at what the demand is for, from their perspective, and lay down the basis and a vision towards creating a practical and performant blockchain trade infrastructure.
First, we summarise the Context of today’s market for DLTs. Then, we look at a Vision of the end-user’s needs, and how to meet them. Then, we review an Architecture to meet the market demands.
Finally a quick Comparison with known systems and Concluding remarks. For more technical details on the EOS.IO software, readers are referred to “EOS.IO Technical White Paper” (Larimer 2017).
Want to find a web3 job?
| Job Position and Company | Location | Tags | Posted | Apply |
|---|---|---|---|---|
.png) | Remote |